Blockset described on this wiki is deprecated since 2012.
For Model Based Design (MBD), use the free MPLAB Device Blocks for Simulink, tool from Microchip.
Updated Rapid Control Prototyping (RCP) custom projects are published at: https://lubin.kerhuel.eu.
Difference between revisions of "DsPIC Block/CAN Transmit"
LubinKerhuel (talk | contribs) |
LubinKerhuel (talk | contribs) m (LubinKerhuel moved page Block/CAN Transmit to DsPIC Block/CAN Transmit: Block is a special page, creates many issues) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
=Dialog Box Parameters= | =Dialog Box Parameters= | ||
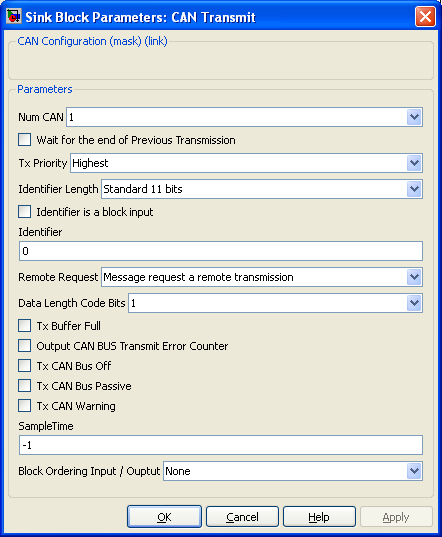
| − | + | [[Image:Block_CANTransmit_DialogBox.png|thumb|right|450px|CAN Transmit Dialog]] | |
==Num CAN== | ==Num CAN== | ||
Ref to the CAN peripheral being configured (some PIC have two CAN bus) | Ref to the CAN peripheral being configured (some PIC have two CAN bus) | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
==Info== | ==Info== | ||
Information | Information | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | <comments \> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:30, 3 May 2015
Write data to a CAN bus
The CAN Transmit block allow to send CAN message containing between 1 and 8 bytes on a CAN Bus. The configuration of the BUS parameters are set using the CAN Configuration block. The two internal buffer of the CAN peripheral are used.
Contents
Dialog Box Parameters
Num CAN
Ref to the CAN peripheral being configured (some PIC have two CAN bus)
Wait for the end of Previous Transmission
When unchecked, the CAN Transmit block try to place the CAN Message into one of the two buffer available on the CAN peripheral. If both buffer are not empty, the message is not sent.
When checked, the CAN Transmit block try to place the CAN Message into one of the two buffer available on the CAN peripheral. If both buffer are not empty, the block will wait until one of the two buffer becomes empty (ie, once the message it contains is sent on the CAN bus). The empty buffer is then filled with the CAN Message and the execution of others blocks continue..
Tx Priority
Each message is assigned to a priority. When the two buffer of the CAN Peripheral contains two message, the message with the highest priority is being sent first. Four priority level exist :
- Highest
- High
- Low
- Lowest
Identifier Length
The message identifier is being code eigher with
- Standard 11 bits identifier
- Extended 29 bits identifier
Identifier is a block input
If checked, the Message Identifier is defined throught a block input. If unchecked, the Message Identifer is defined inside the dialog box (An Identifier parameters appears)
Remote Request
The message set the Remote Request bit. (see CAN doccumentation)
Data Length Code Bits
Length of the message you want to send. The message is contain up to 8 bytes. If message length is greater than 1, a vector of the message length is connected to the block input. The simulink bus creator block can be used to build a vector with the desired length.
Error flags
Each of these checkbox output the requested binary error flag.
- Tx Buffer Full
- Tx CAN Bus Off
- Tx CAN Bus Passive
- Tx CAN Warning
Output CAN BUS Transmit Error Counter
The Transmit Error Counter output the internal CAN Transmit Error Counter. See CAN doccumentation for precision about Error Counter.
Sample Time
Sample time of the block. -1 for inherited
Block Ordering Input / Output
If you want to force the execution order of blocks that are not connected, this option allow to add either an input, an output or both to the block. These virtual connection allow to force the ordering of the blocks.
Info
Information
<comments \>